Binyamin Appelbaum writes:
Inflation is widely reviled as a kind of tax on modern life, but as Federal Reserve policy makers prepare to meet this week, there is growing concern inside and outside the Fed that inflation is not rising fast enough.
The Fed has worked for decades to suppress inflation, but economists, including Janet Yellen, President Obama’s nominee to lead the Fed starting next year, have long argued that a little inflation is particularly valuable when the economy is weak. Rising prices help companies increase profits; rising wages help borrowers repay debts. Inflation also encourages people and businesses to borrow money and spend it more quickly.
Weighed against the political, social and economic risks of continued slow growth after a once-in-a-century financial crisis, a sustained burst of moderate inflation is not something to worry about,” Kenneth S. Rogoff, a Harvard economist, wrote recently. “It should be embraced.”
The Fed, in a break from its historic focus on suppressing inflation, has tried since the financial crisis to keep prices rising about 2 percent a year. Some Fed officials cite the slower pace of inflation as a reason, alongside reducing unemployment, to continue the central bank’s stimulus campaign.
Critics, including Professor Rogoff, say the Fed is being much too meek. He says that inflation should be pushed as high as 6 percent a year for a few years, a rate not seen since the early 1980s. And he compared the Fed’s caution to not swinging hard enough at a golf ball in a sand trap. “You need to hit it more firmly to get it up onto the grass,” he said. “As long as you’re in the sand trap, tapping it around is not enough.”
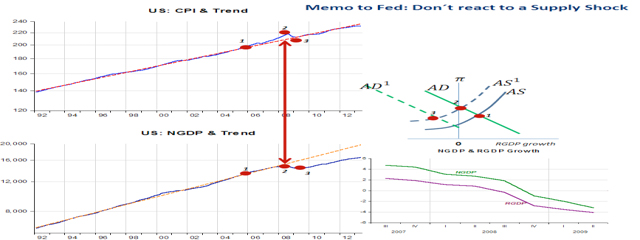
Recently I showed that during the “Great Moderation” all the usual “targets” – “IT”, PLT” or “NGDPLT” were observationally equivalent. But since the crisis erupted we received the “information” that the “mother of all targets” is “NGDPLT”.





Be the first to comment on "Inflation… Trapped!"