Javier Ibáñez de Aldecoa Fuster (CaixaBank Research) | 2020 has now been left behind; a year that will be remembered in the tourism industry as the toughest in recent history. In 2021, the fight against the pandemic continues and restrictions on movement and trade are still preventing normal economic activity, hitting tourism-dependent businesses particularly hard. However, the roll-out of the vaccines will provide a turning point once immunity is achieved among the population most at risk. Our projections point to a strong recovery in the sector during the second half of the year, resulting in tourism GDP growing by 80% annually, once again becoming one of the driving forces for the Spanish economy.
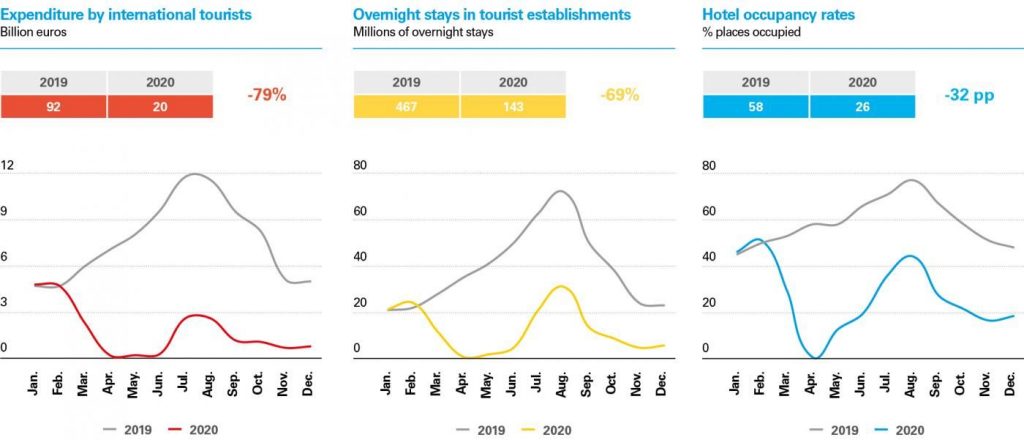
Examining the 2020 figures provided by the National Statistics Institute, summarised in the charts below, it is clear that the tourism industry has suffered an unprecedented shock. Expenditure by international tourists for the year as a whole plunged to €20 billion, down 79% from €92 billion in 2019. Even during the best tourist months after the start of the pandemic, namely July and August, the falls in international tourist expenditure remained at around 80% year-on-year.
Data from hotel and non-hotel occupancy surveys reveal that tourist accommodation is one of branches in the industry that are suffering the most from the consequences of the pandemic.1 Total tourist overnight stays in hotel and non-hotel accommodation fell by 69% year-on-year, despite the better performance of domestic demand in relative terms. The hotel occupancy rate remained very low for the year as a whole (with an annual average of 26%), dragging hotel revenue per available room down by 68% annually.
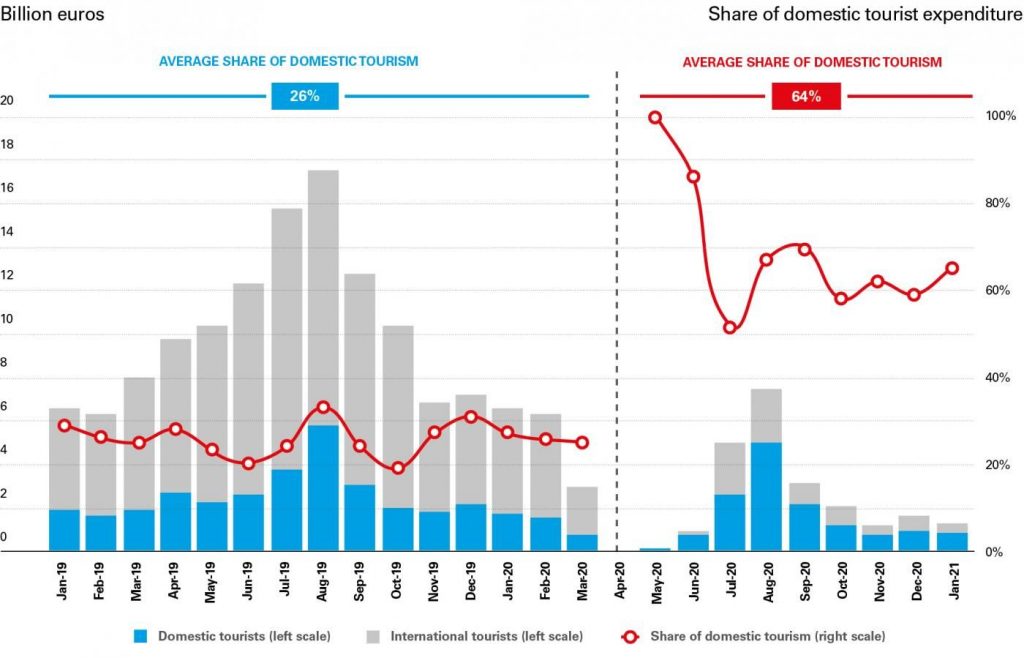
One of the few positive notes in the 2020 figures is that domestic demand has proved to be a powerful support for the industry when movement restrictions are eased. Nevertheless, domestic tourist expenditure has also fallen sharply, especially since last October when the autonomous regions began to restrict movement to within their borders, limiting almost all domestic tourism. According to our estimates, domestic tourist expenditure fell by 45% in 2020, considerably less than international tourism. Domestic demand, which traditionally accounts for a quarter of the total, therefore generated 64% of the overnight stays after the outbreak of COVID-19. It is also worth noting that, during August when movement was not so restricted, spending by domestic tourists only fell by 13% year-on-year. This paints a relatively positive picture for the second half of 2021, by which time the population at risk should have been vaccinated and restrictions on movement will begin to be withdrawn.
Real-time situation of the tourism sector
At present, the state of the tourism industry is extremely volatile. For this reason, it is of vital importance to have an analysis of the situation that is as up-to-date as possible, in spite of the delay in publishing official statistics. To this end, we carry out a real-time analysis, using big data methodology, of the card payments made via CaixaBank’s point-of-sale (POS) terminals.
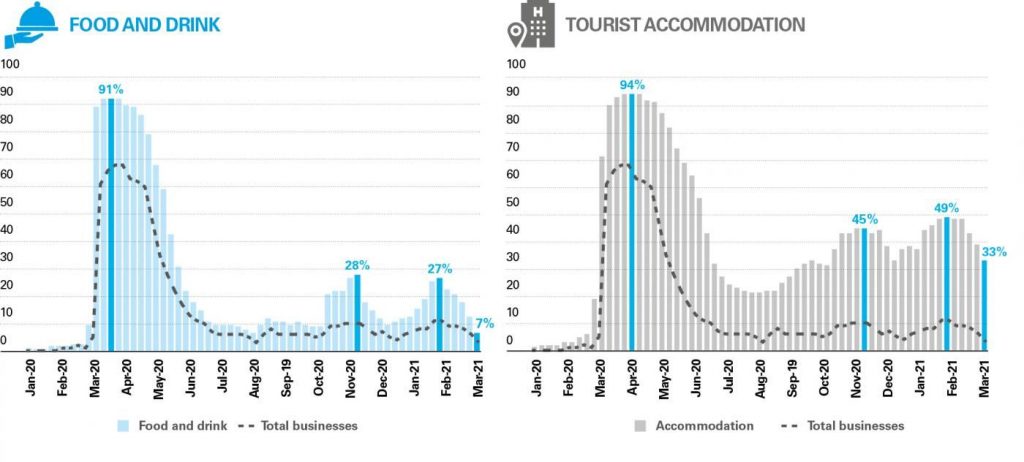
According to our indicator, the beginning of the year has been severely affected by the third COVID-19 wave in January and part of February and the tightening of restrictions to combat this. More recently, the data point to an incipient upswing in the turnover of some tourism businesses following the easing of restrictions on hospitality in many autonomous regions. As suggested by CaixaBank’s POS card expenditure data for the first half of March, the POS turnover of tourism-dependent retailers was still 52% below the level recorded during the same period in 2019. In this respect, it is worth noting the continuing sharp drop in POS turnover for accommodation and travel agencies, down by 83% and 91%, respectively. On the other hand, restaurant business POS terminal expenditure, which has suffered considerably from measures to contain the second and third waves of COVID-19, has picked up notably in recent weeks, going from drops of 40% at the end of January compared to the same period in 2019 to a fall of «just» 12%.
The improvement in the conditions observed for the food and drink industry, mainly in restaurants and bars, has led many businesses in this branch to reopen their doors in recent weeks, something that could be very important to recoup the jobs lost. To track inactivity in real time, we have calculated the proportion of businesses that have gone from recording payments via their CaixaBank POS terminals in 2019 to recording no activity in 2020 and 2021. As can be seen in the chart, according to this indicator the proportion of inactive bars and restaurants during the second week of March 2021 stood at 7%, 10 pp lower than at the end of January 2021. For its part, tourist accommodation reported 33% of inactive businesses, a very high level although significantly better than the situation observed at the end of January.
Outlook for the spring season
Looking ahead to the coming months, the outlook is not positive. If we analyse Google searches for trips to Spain carried out in our main source markets, we can see that interest is still low and, therefore, the prospects for foreign arrivals in the short term are moderate. As can be seen in the chart, according to our analysis searches by international tourists were 53% below the benchmark level. However, tourism will depend on how the pandemic evolves and it is to be expected that, once we are able to ease restrictions on international travel, interest will pick up rapidly. Consequently, the experience after the coordinated withdrawal of EU border restrictions in June 2020, when the interest of tourists in travelling to Spain went from 60% below the benchmark to just 5%, revealed that European tourists still want to travel in spite of the restrictions and, in 2021, if these restrictions are eased, the interest in travelling to Spain will pick up. Of particular note is the sharp rise in Google searches in mid-March 2020, the result of internet users’ interest in the border restrictions introduced as a result of the first state of emergency.
It is vitally important to prevent a fourth wave of infections. Otherwise, the sector could once again suffer a situation similar to that experienced at the beginning of the year, when turnover fell by around 70% for several weeks. At the time of going to press, the situation in the main European countries remains very delicate and there has been another spike in the number of daily infections, indicating there is still a high risk of outbreaks in Europe.
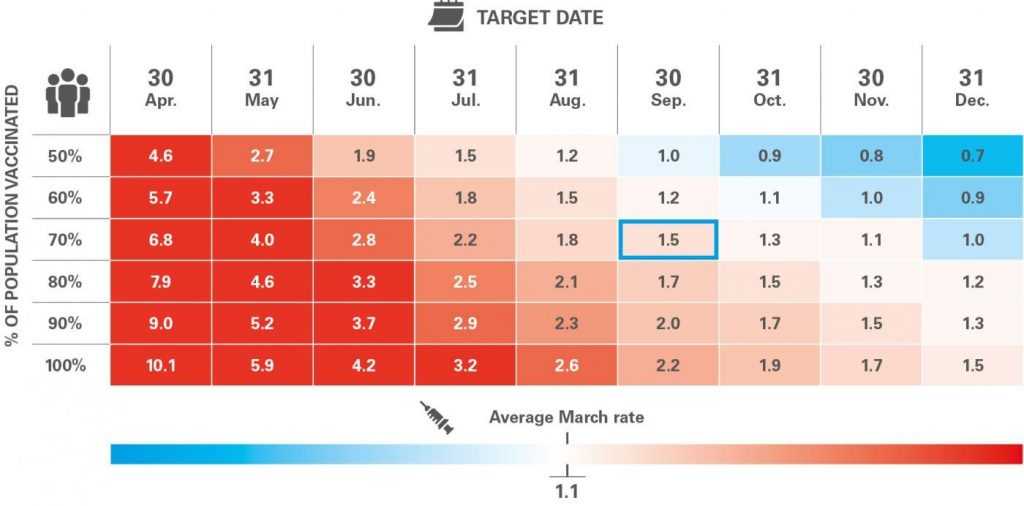
The rapid distribution and administration of vaccines is a key factor for the recovery to begin in the tourism sector and the economy as a whole. According to the European Commission’s target reflected in Europe’s vaccination plan, 80% of health workers and the population aged over 80 should have been vaccinated by the end of March, while the target of vaccinating 70% of the adult population, which should bring about herd immunity, has been set for the end of September.5
Although there have been delays in distributing the vaccines, the September target is likely to be met. In March, the average vaccination rate for the Spanish population was around 1.1 million doses per week. As can be seen in the table, this rate needs to be speeded up by at least 40%, up to 1.5 million doses per week, in order to achieve the target of herd immunity by the end of the summer. While this is a significant increase, it is nevertheless feasible considering the following: in the last month, Spain’s vaccination rate has already risen by 45%, the safety of the AstraZeneca vaccine has been confirmed and the first supplies of the Janssen/J&J vaccine arrived in April.
In the short term, the key for the tourism sector is to immunise the over-60s before the summer. This group accounts for just 20% of the infections but two-thirds of the severe cases of COVID-19 and nearly 95% of the deaths. Increasing the vaccination rate to 1.5 million doses per week would achieve immunity for 90% of the population at risk by May. Once this milestone has been reached, the pressure on hospitals would noticeably ease and COVID-19 containment measures could be relaxed, helping to substantially improve the movement of both domestic and international tourists.
Given that this first milestone looks likely to be reached, CaixaBank Research expects tourism expenditure to recover strongly as from the second half of the year. Specifically, our scenario is based on the hypothesis that the restrictions on movement and business will start to ease considerably from May onwards, when a significant part of the population at risk will finally be immunised, and that a further move towards normalising the situation will be possible in September, once herd immunity is achieved. Similarly, the introduction of the health passport from June, as proposed by the European Commission, will make it easier and encourage people to travel during the summer season.6 Also, the rapid (albeit brief) improvement in tourist flows during the months of July and August in 2020, when movement was permitted but social distancing measures were still in place, suggests that tourism will recover strongly once restrictions on movement in Europe are eased.7
Based on these three assumptions, and acknowledging there is still a great deal of uncertainty surrounding our scenario, we expect international tourism expenditure in 2021 to increase 2.3 times compared with the 2020 levels, leaving it 45% below the 2019 levels. As for domestic tourist expenditure, we expect this to grow by 30% year-on-year, 25% below the 2019 figure (–45% in 2020). As far as the summer season is concerned, the outlook is relatively positive: we expect international expenditure to limit its decline compared with summer 2019 to 27% while, in the case of domestic tourism, the drop is expected to be 16%.
As a result of these spending figures, we expect tourism GDP to be about 40% below its pre-COVID level in 2019, a recovery of 80% compared with 2020.This recovery would directly contribute 1.9 pp to the growth of Spain’s economy. Although there is still a lot of uncertainty regarding 2022, the progress being made by the vaccination roll-out invites us to remain positive. We therefore believe that the population’s herd immunity will help normalise the movement of tourists in Spain and Europe. In this case, the sector would regain a level of activity that is still below but closer to those of 2019, in any case enough to ensure the profitability of the businesses that make up the tourism industry.
Although the sector’s long-term sustainability is beyond doubt, the role played by the government will be crucial during the period of gradual recovery that still lies ahead. It is therefore important to highlight the importance of economic policy in 2021 as a whole, which must continue to adapt rapidly and effectively. In this respect, we believe the furlough scheme should be extended until the recovery consolidates. It will also be important to take advantage of the flexibility provided by the extension of ICO bonds and their grace periods. Moreover, the direct aid received by the sector will be very useful to ensure the survival of businesses that will become profitable once people can travel again. Consequently, the 7 billion euro package launched by the central government and the funds available to boost solvency (the 10 billion managed by SEPI plus the 4 billion accompanying direct aid in the last package) are a move in the right direction. Finally, the Next Generation EU (NGEU) funds will also be important when it comes to supporting improvements in digitalisation, sustainability and infrastructures, investments which are currently difficult for such a hard-hit tourism industry to undertake but vital in order to survive this crisis whilst maintaining our status as the most competitive tourist destination in the world.





