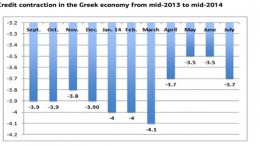
Don’t Worry, Corporate Leverage Only Just Back To Level Of 2007
AXA IM | Companies have re-leveraged their balance sheets since the global financial crisis (GFC), driven by low borrowing costs. Although heightened, corporate leverage is not currently excessive in developed markets, although we see signs of concern in emerging markets. In this note we assess whether we should be concerned about corporate leverage at current levels.